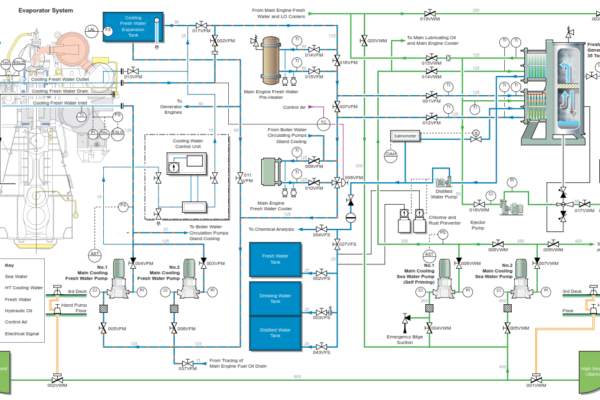
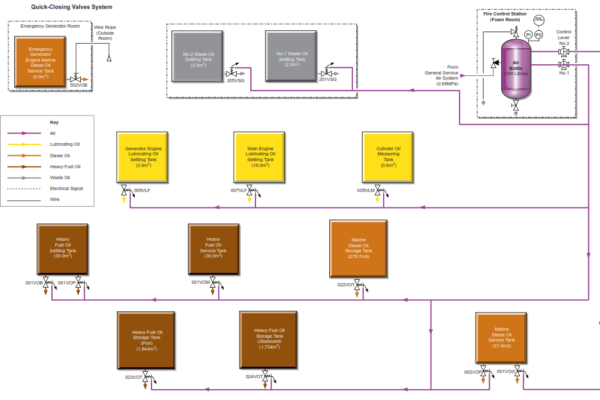
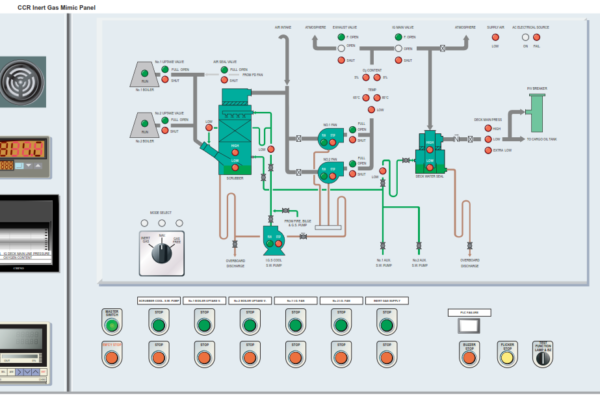
FRESH WATER EVAPORATOR
The fresh water generator (evaporator) installed in the engine room utilizes the heat available from the main engine jacket cooling water system to produce fresh water for use on-board the vessel. In doing so the evaporator acts as a cooler for the main engine jacket