Aim
To understand the construction of various types of ships. In this module we will study the salient features of construction in different types of ships.
Oil Tanker
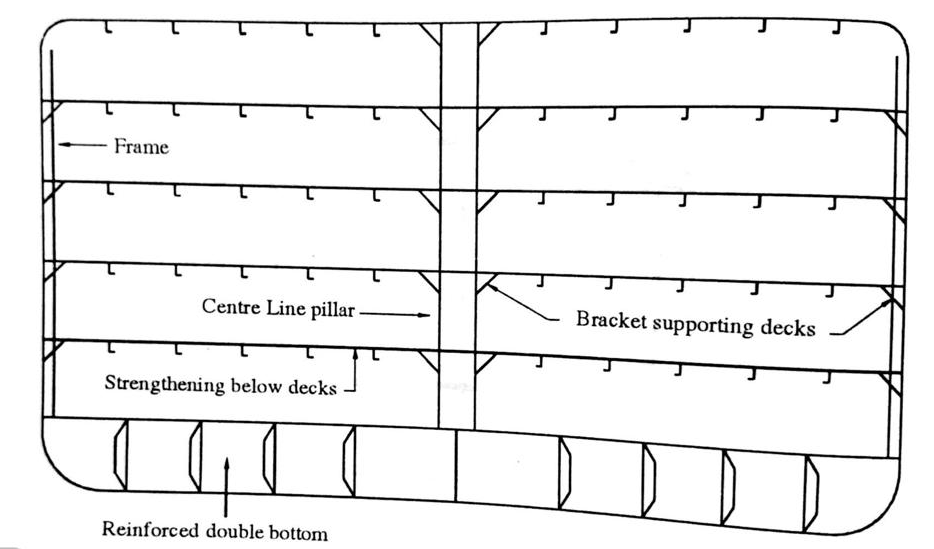
Twin longitudinal bulkheads divide the tank section into port, starboard and centre tanks. In most old tankers there is no double bottom. Longitudinal features strengthen the main deck and the bottom. In small and medium sized tankers the side shell may be stiffened by transverse frames but if the tanker exceeds 150 m in length, the side shell is stiffened by longitudinals. When transverse framing is adopted for the side shell, it is supported by horizontal stringers the number of which will depend on the depth of the tank. The lower ends of the frames are connected by brackets, which extend to cover the round of the bilge and are connected to the adjacent longitudinal, clear of the transverse. The upper ends of the frames are connected to the underside of the deck, clear of the transverses, by brackets.
When longitudinal strengthening is used, the deck and bottom longitudinals have the greatest scantlings since they stiffen the most highly stressed flanges of the ship girder. The upper longitudinals at the side shell have the least scantlings and the size of the scantlings increases uniformly downwards till the bottom longitudinals are reached. The important feature of longitudinal strengthening is that the deck and bottom longitudinals are continuous and pass through the transverse bulkheads. High tensile steel longitudinals have to be continuous, irrespective of the length of the vessel. The construction of the new generation double hull tankers is same as explained earlier, except that they also have a double bottom, which is longitudinally framed, and the double hull side space has stiffened plate transverses in line with each double bottom floor.
Dry Cargo Vessel
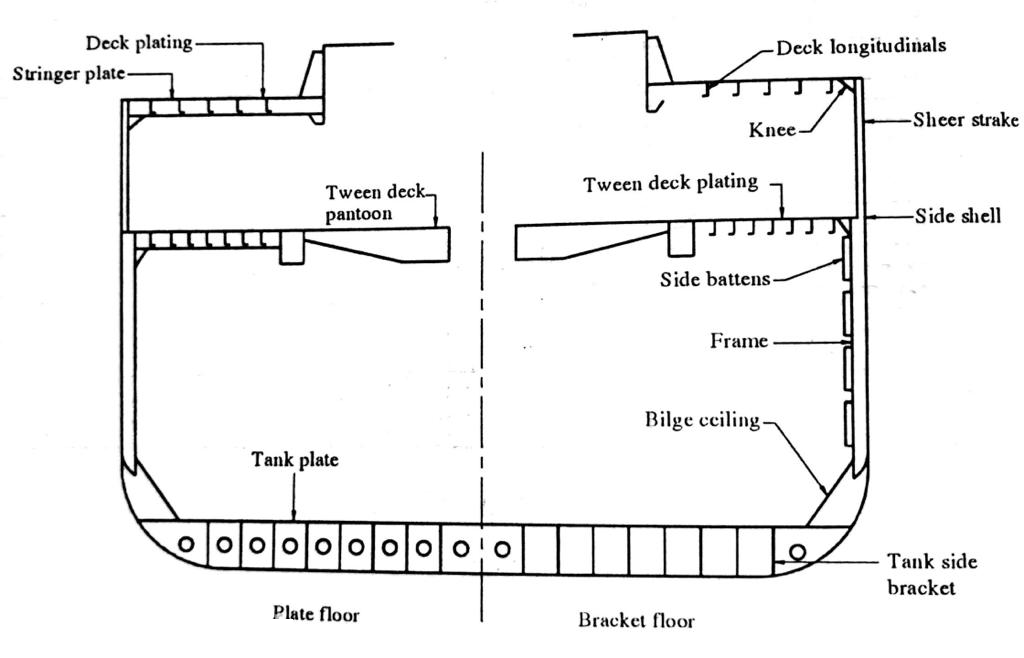
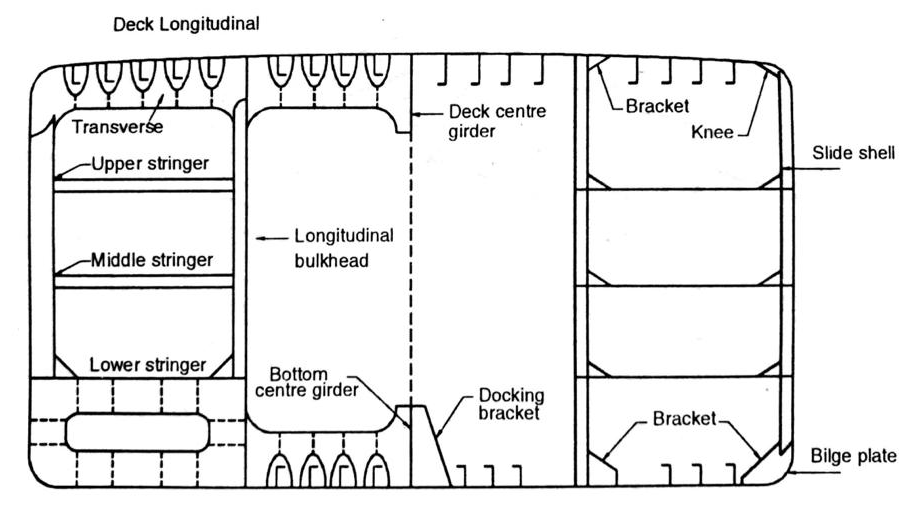
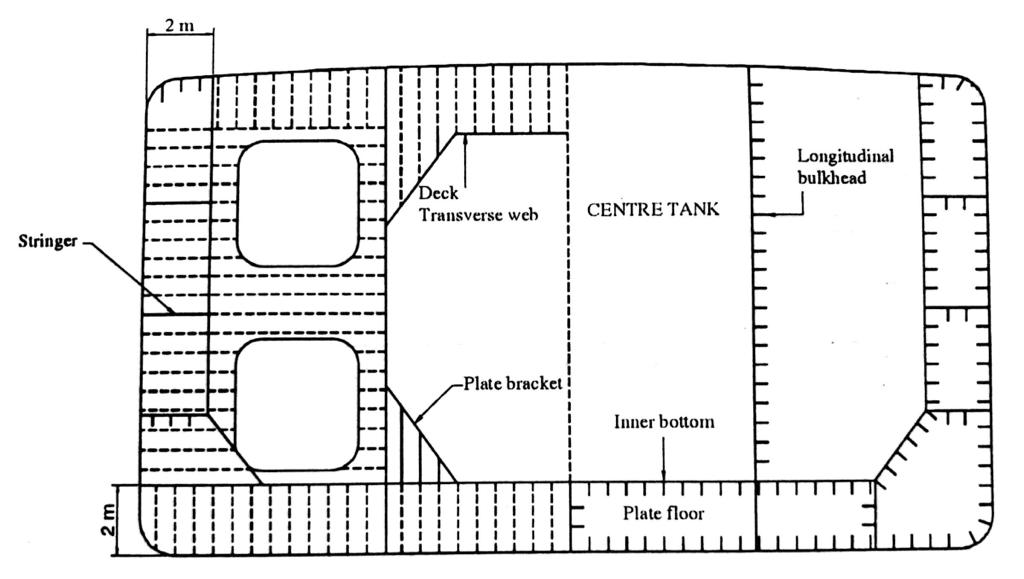
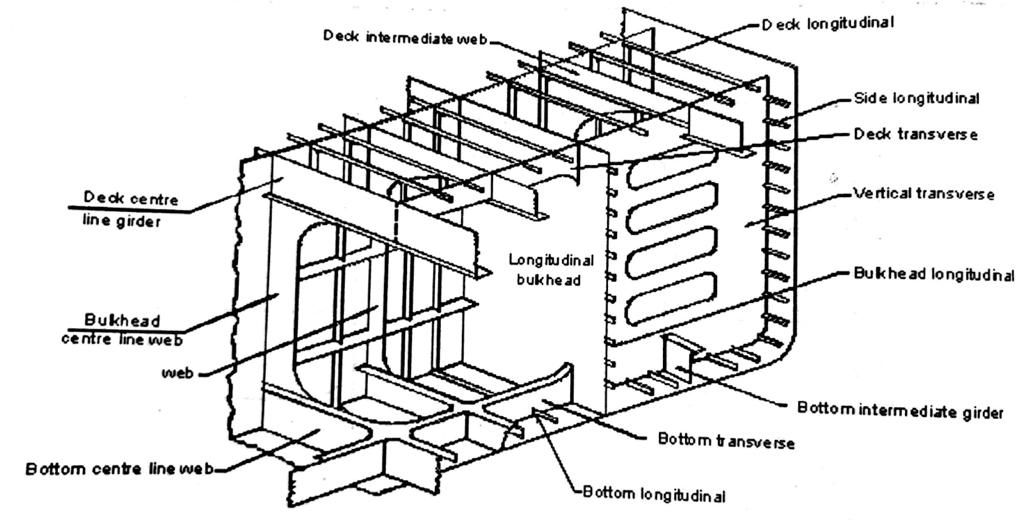
This type of ship normally has transverse framing, which consists of main and hold frames with brackets at the top and at the bottom. They have lighter tween deck frames, which have brackets only at the top. Scantlings of the main transverse frames are primarily dependent on their position, spacing and depth. In way of deep tanks or bunker tanks the size of the side frames is increased except where supporting side stringers are fitted. Frames which have to bear heavy load like the hatch end beam or below the cranes /derricks, have increased scantlings.
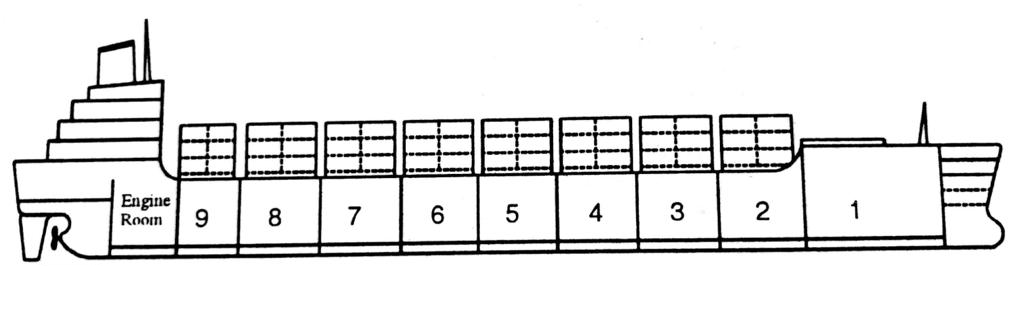
Container Vessel
These ships are designed to carry containers. The hull structure is either a single hull with heavy web frames or cantilevers or a double hull as shown in the figure. Hatchways are as large as possible covering up to 80% of the breadth of the main deck.
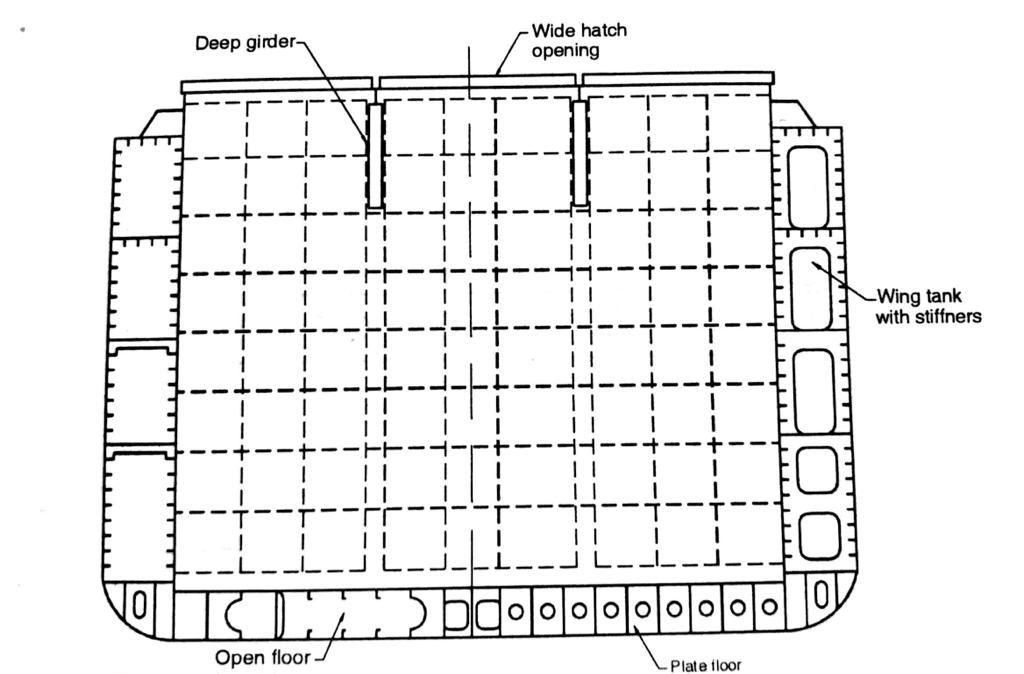
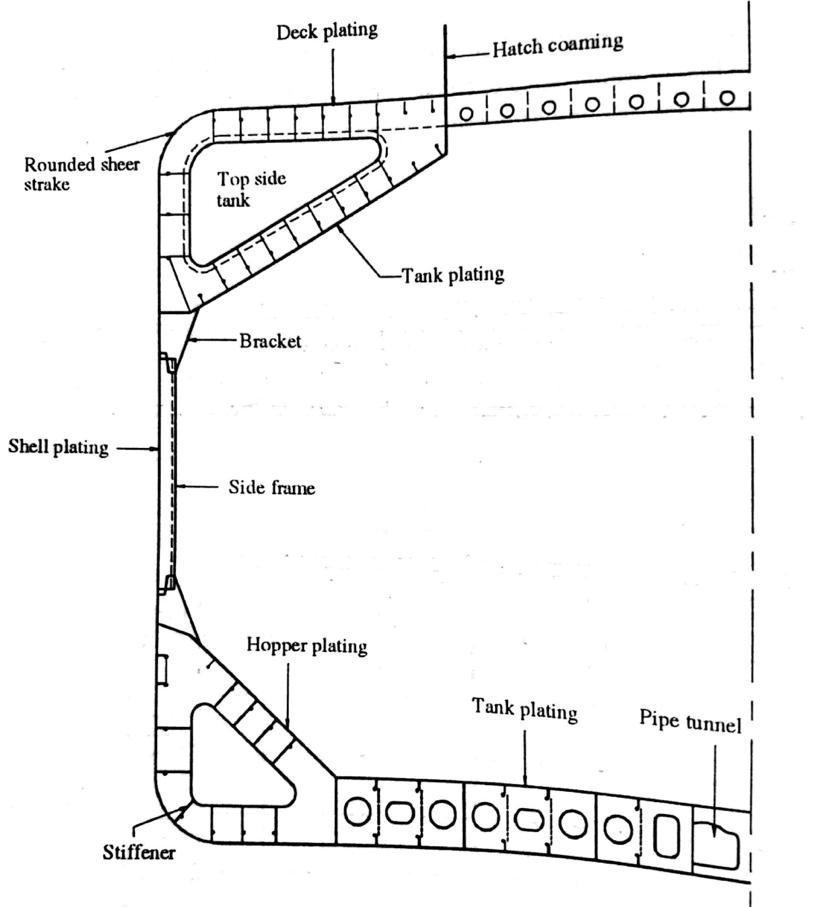
Bulk Carrier
These Ships are designed to carry dry cargo in bulk. The structural feature includes upper wing tanks, wide hatchways, and strengthened inner bottoms.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) tankers
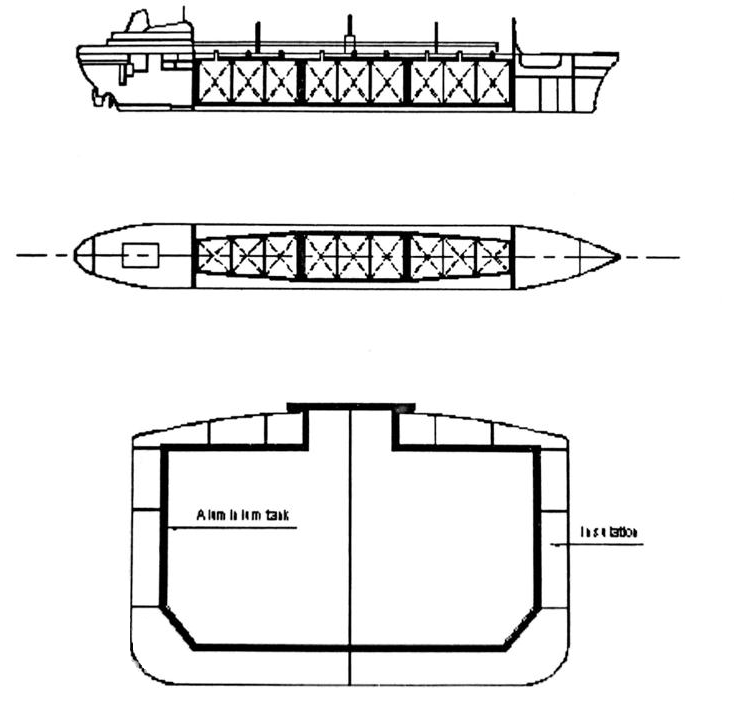
Natural gas can be liquefied at atmospheric pressure if cooled to a temperature of -164°C. The volume of the liquid is 0.158% of the original volume of gas which is a considerable reduction in the size of the storage tanks.
If LNG were loaded into an ordinary tanker, two things would occur which would have serious effects. Firstly the very low temperature of the cargo would cause the mild steel structure to crystallise and fracture. Secondly the heat entering the cargo spaces through the hull would raise the temperature of the liquid above its boiling point causing excessive evaporation and “boil-off” losses. The construction and the materials used in the construction of a LNG tanker must take both of these points into account. A steel double hull structure is provided to stiffen the hull and provide adequate water-ballast space. Between the inner hull and the tank is placed the insulation, usually balsa wood.
The inner surface of the tank must be constructed of a metal, which will stand up to these low temperatures. Materials used include stainless steel, aluminium and Invar. In case the tank fractures a secondary barrier of plywood is fitted to contain any spillage of LNG.
Ro Ro Vessel
These ships fall into two main types. The first is mainly concerned with the transport of passenger vehicles and must provide separate spaces for vehicles and passenger accommodation. The other type carries trailers with cargo. Many vessels are a mix of both types. Both types must be provided with suitable access for the vehicles to be driven on board. This is for the vehicles to be driven on board. This may be through bow, stern or side doors. Ramps or elevators often provide internal access between decks.