Cargo oil tanks must be water washed, purged and gas freed prior to inspection. Cargo oil tanks must NEVER be entered when inerted.
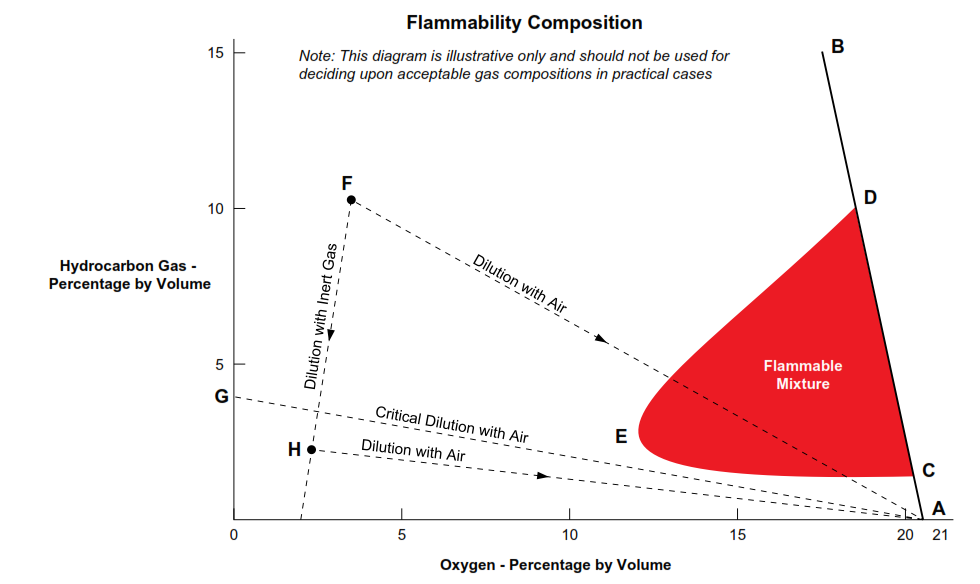
Prior to gas freeing any COT or gaseous space, the hydrocarbon content must be below 2% Hc, thus ensuring that the space will not pass through the flammable envelope as the oxygen percentage increases. (See Flammability Composition Diagram – Hydrocarbon Gas/Air/Inert Gas Mixture.)
It is important to locally isolate tanks that are to be gas freed, so that inert gas cannot enter these tanks from adjacent, inerted tanks, or conversely that air cannot enter inerted tanks. All portable gas measuring equipment must be tested and calibrated with their results logged.
The first stage in the gas freeing process is called purging. Common practice is to purge a couple of tanks at a time and monitor the gas emitted until it is below 2% Hc. This method is termed replacing a tank atmosphere by DILUTION.
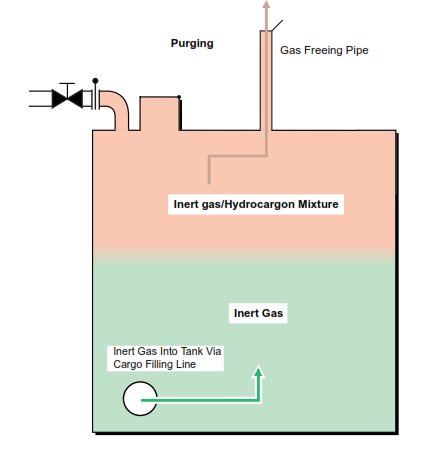
The inert gas at high velocity is injected through the cargo main suction valves and mixes with the gaseous atmosphere, which is then vented through the gas freeing pipe fitted on each tank. The configuration of the IG crossover onto the cargo main does not allow venting via the mast riser.
If only one, or a few tanks are to be purged in preparation for gas freeing, then these tanks must be isolated from the rest of the cargo oil tanks by closing the IG inlet block valve.
The weather conditions must be monitored during the gas freeing operation, if an electrical storm is in the vicinity then the operation must be stopped and the system shut down.
GAS FREEING FOR ENTRY PROCEDURE
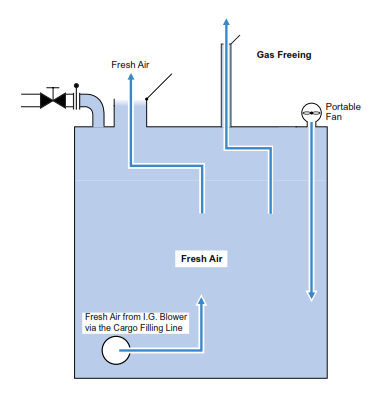
Procedure to gas free a tank for entry.
a) Before any work can take place a work plan must be drawn up and distributed to the necessary personnel which must be read and understood. All portable gas measuring equipment must be tested and calibrated and their results logged.
b) All cargo tanks hydro carbon content to be less than 2% VOL to commence gasfreeing.
b) Open branch IG of all cargo tanks on port side and close branch IG of all stbd tanks.
c) Open gas freeing vent on PV valve of all cargo tanks on starboard side.
c) IG system to be started on gasfreeing mode and let the fresh air enters the Port cargo tanks via the branch IG line.
d) Open cargo tank main valves . Hydrocarbon/air mixture will flow from port to starboard tank and will vent out through gas freeing outlet on PV valves of stbd tank.
e) Once the cargo tank hydrocarbon level drops to 30% LEL then use hydroblowers for that specific tank to carry out gas freeing. At that time close the IG branch valve and tank valves. Open tank domes and manhole covers for more effective venting.
f) Monitor the tank atmosphere for oxygen until the readings are 21% O
h) Carefully monitor for LEL and ensure that the reading is consistently below 1% but preferably zero.
A Responsible Person is to Take Charge
A responsible officer will take charge of the entry operation, this person will be appointed by the Master, Chief Engineer or chief officer.
Potential Hazards to be Identified
Oxygen deficiency and/or the presence of toxic substances or flammable vapours.
Space Prepared and Secured for Entry
The space to be entered is to be secured against the ingress of dangerous substances. Valves are to have a positive method of displaying if open or shut, and of preventing them from being operated while entry is taking place. The OOW on watch on the bridge, or on the main deck, is to be informed of any tank entry.
Atmosphere Tested
The COT atmosphere is to be tested for both oxygen and LEL, at different levels and sections, and if remote checking cannot take place, entry is to be made wearing breathing apparatus, in a fully controlled manner. A Permit to Work Certificate, of limited duration, will be required.
Entry into a space, without the use of breathing apparatus, is only permitted when the oxygen content is 21%, and the flammable gas content is nil. Where readings have been steady for some time, up to 1% LEL is acceptable in conjunction with the 21% oxygen.
Permit to Work Completed
A permit to work must be completed before entry. The permit should be of limited duration and should, in any case, not have a validity in excess of 24 hours.
Pre-Entry Preparations Made
The space must be thoroughly ventilated and the atmospheres tested and found safe for entry without breathing apparatus. Rescue and resuscitation equipment is to be at the entrance to the space, along with a responsible person who will maintain constant and full communications with the personnel throughout the time they are in the space. They should also maintain communications with the OOW.
All equipment is to be checked as being intrinsically safe.
Procedures During Entry
Ventilation is to be continued during the entry period. Should the ventilation fail, the operation is to be stopped and personnel in the tank are to return to the deck immediately.
The atmosphere must be tested at regular intervals to verify that is still safe. Careful monitoring of personnel in the tank is to be carried out. Should the responsible person note any adverse signs he is to issue the recall signal immediately and advise the OOW, who will sound the alarm and summon assistance.
In a similar manner, should any person in the tank feel adversely affected in any way, they are to warn their companions and vacate the tank immediately.