Modern ships today are equipped with fresh water generators. They enable an unlimited supply of fresh water to be produced. With modern efficient fresh water generators, ships normally take a minimum amount of fresh water and produce the rest on board.
Every crew uses about 70 litres of water a day for bathing, washing, drinking and other domestic uses. Clean fresh water is also required for boiler steam plants and the engine cooling system. Average consumption for a ship with 20 crew can be between 15 to 20 tonnes per day.
Shore water is not preferred because it has impurities like chlorine and suspended particles. Impurities in the water can form scale on heat transfer surfaces, reducing the heat transfer efficiency of engine and boiler. Therefore there is a need for a freshwater generator to produce high quality water onboard ships.
The concept of a fresh water generator is simple; sea water is evaporated using a heat source, separating pure water from salt, sediment and other elements. Fresh water generators often use the diesel engine jacket as a heat sourve, although steam can also be used as a heat source. Because freshwater often use existing heat to run, the cost of operation is low.
Fresh water generator principle
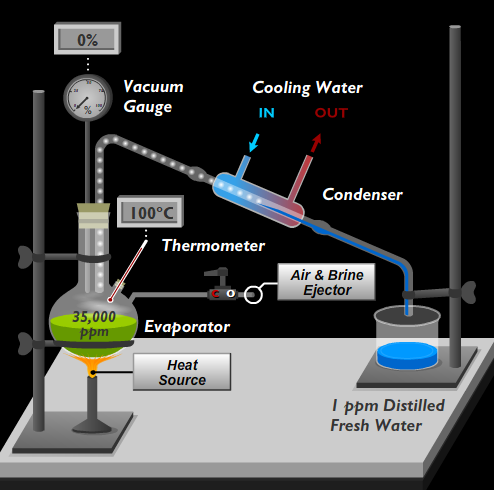
Water boils at 100°C at atmospheric pressure. When pressure is reduced to below the atmospheric pressure, the boiling temperature is also reduced.
This is the principle on which the fresh water generator works.
In other words the boiling point can be brought down as low as 27°C if the pressure is sufficiently reduced using an educator.
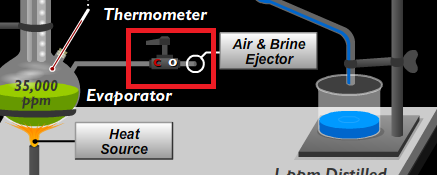
Open or close the valve to reduce or increase the pressure in the evaporator.
Air and Brine Ejector
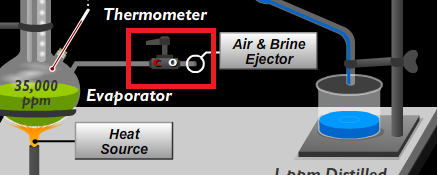
Eductors are devices employed to remove air and liquid from the systems. In the fresh water generator, they are used to reduce the pressure as well as remove the brine.
Eductors use a high velocity jet of sea water to lower the pressure in the chamber around the converging nozzle. Sea water is supplied to the converging nozzle at a relatively low velocity and exists the nozzle at a high velocity.
As the sweater leaves the nozzle and passes through the diffuser. Pressure in the suction chamber decreases causing a suction effect. Air and brine from the fresh water generator is drawn in discharged overboard.
Heat Source
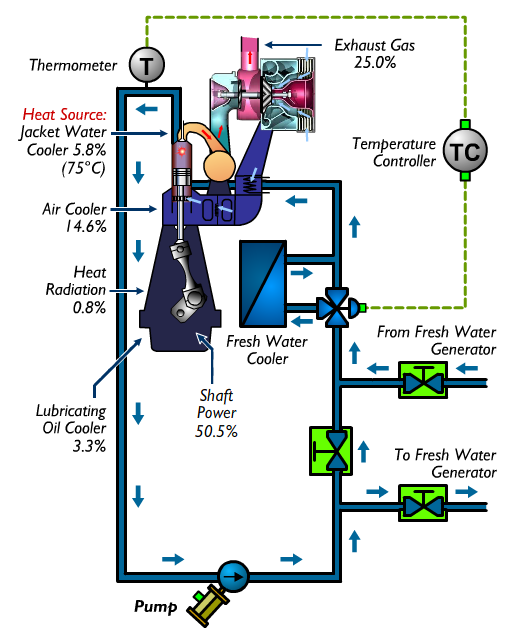
The heat balance diagram of the main engine shows that 6% of the waste heat is available heat is available as a heat source for evaporating the sea water in the fresh water generator.
Salinometer

The salinometer and salinity cell, in conjuction with the solenoid operated dump valve and the spring loaded valve, control the quality of the water pumped to the fresh water tanks.
The salinity cell, in conjunction with the salinometer, measures the conductivity of the water produced by the evaporator which is proportional to the amount of salt in the distillate. The salinometer has a scale of 0 to 20 ppm (parts per million).
It has an alarm set, alarm light and alarm buzzer on the local panel and also sends an alarm signal to the main control station console.
The normal alarm setpoint is 2 ppm. When an alarm condition is realized, the solenoid operated dump valve (opens) allowing distillate to be dumped into the bilges, This allows the spring loaded valve to close, ensuring contaminated water is not sent to the potable water tanks.