AIR MASS
When air remains over an area of the earth’s surface for several days, its physical properties are affected by those of the earth’s surface.
If the surface is WARM & WET, the overlying air will become WARM & HUMID.
Eg. Air over the WARM GULF STREAM.
If the surface is very HOT & DRY, the overlying air will become HOT & DRY.
Eg. Air over the LAND SURFACE in the INTERIOR of AUSTRALIA.
A change in the pressure distribution will cause the air to move away from the SOURCE REGION.
However, these characteristics are modified slowly & air which, for e.g. started off WARM & MOIST, tends to remain WARM & MOIST, even though it moves over a COLD DRY surface.
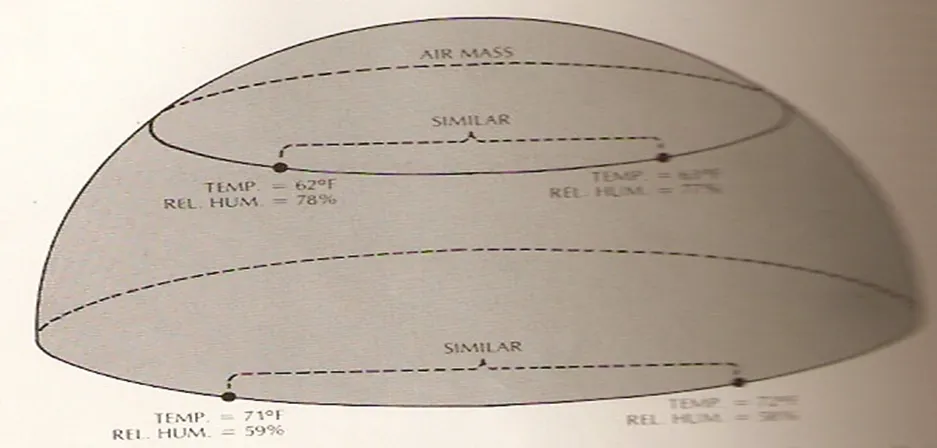
AN AIR MASS IS THUS DEFINED AS A WIDESPREAD BODY OF AIR THAT IS ALMOST HOMOGENEOUS THROUGH ITS HORIZONTAL EXTENT, PARTICULARLY WITH REFERENCE TO TEMPERATURE & MOISTURE DISTRIBUTION; IN ADDITION, THE VERTICAL TEMPERATURE & MOISTURE VARIATIONS ARE ALMOST THE SAME OVER ITS HORIZONTAL EXTENT.
Thus AIR MASS can be defined as a huge DOME OF AIR (enveloping many thousands of cubic miles), in which the TEMPERATURE & HUMIDITY (or MOISTURE) conditions in a horizontal plane are very similar.
AIR MASS CHARACTERISTICS ARE DETERMINED BY 3 PRINCIPAL INFLUENCES
1. Nature of SOURCE REGION from which the AIR MASS obtains its original characteristics & whether or not its movement after leaving the SOURCE REGION takes it into a WARMER or COLDER environment.
2. The changes that occur within the AIR MASS as it moves away from its SOURCE REGION.
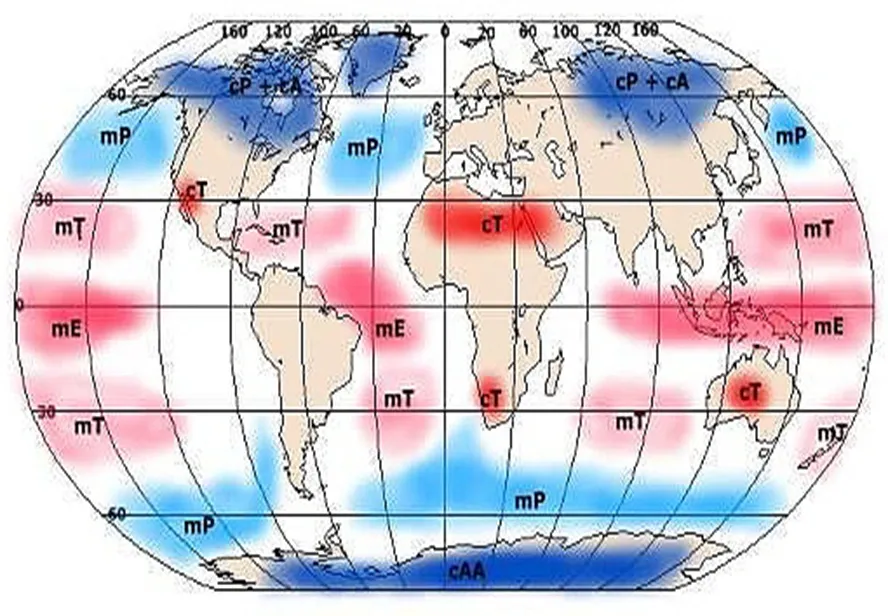
SOURCE REGIONS
AIR MASSES are formed over SOURCE REGIONS where the earth’s surface temperature is nearly uniform & winds are comparatively light. These conditions ensure that the air stays long in the region enough.
WARM AIR MASSES
BOTH HEMISPHERES The principal source regions are the SUB TROPICAL HIGH PRESSURE CELLS & in SUMMER, the great accumulations of WARM SURFACE AIR which characterize the INTERIOR of LARGE LAND MASSES.
COLD AIR MASSES
NORTHERN HEMISPHERE The principal SOURCE REGIONS are the HIGH PRESSURE AREAS of NORTHERN CANADA, SIBERIA & the ARCTIC BASIN.
SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE Except for ANTARCTICA there are NO LARGE COLD LAND MASSES. The SOURCE REGION for most COLD AIR MASSES is the COLD OCEAN surrounding the ANTARCTIC CONTINENT.
Thus AIR MASSES move out from the principal thermal & dynamic HIGH PRESSURE REGIONS – SOURCE REGIONS and move into the LOW PRESSURE REGIONS of convergence.
CLASSIFICATION OF AIR MASSES
AIR MASSES are classified according to TWO primary features
1) GEOGRAPHICAL
The principal SOURCE REGION which describes the TEMPERATURE of that region.
They are POLAR, ARCTIC,TROPICAL & EQUATORIAL
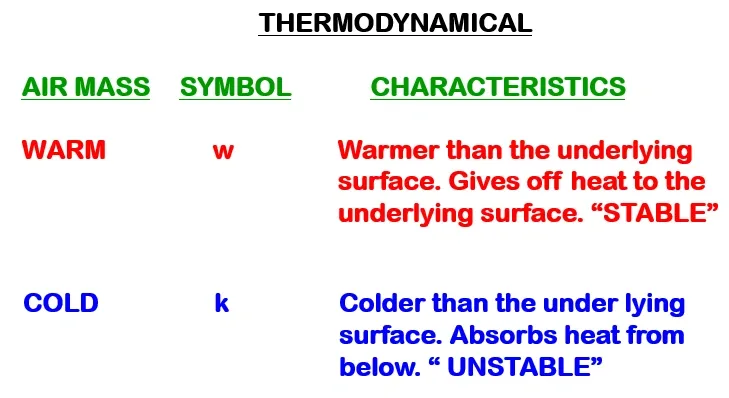
2) THERMODYNAMICAL
Whether the AIR MASS is WARMER or COLDER than the under lying surface.
They are CONTINENTAL & MARITIME
CLASSIFICATION OF AIR MASSES

A)
SOURCE REGIONS:
Western sides of North Atlantic North Pacific & Southern Oceans.
AIR MASS: MARITIME POLAR
SYMBOL: mP
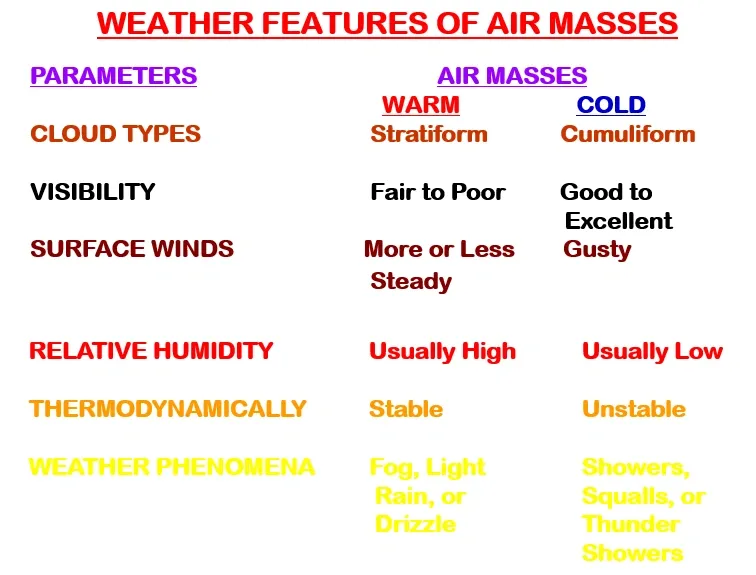
CHARACTERISTICS:
Cold & Humid.
When moves to low latitudes heated from below & instability develops.
Cu with cold showers.
B)
SOURCE REGIONS
Cold High Pressure areas of North Canada & Siberia.
AIR MASS:: CONTINENTAL POLAR
SYMBOL: mC
CHARACTERISTICS
Cold & Dry.
When moves to low latitudes heated from below & instability develops.
Less clouds due to dryness of air. Light snow falls.
C)
SOURCE REGIONS
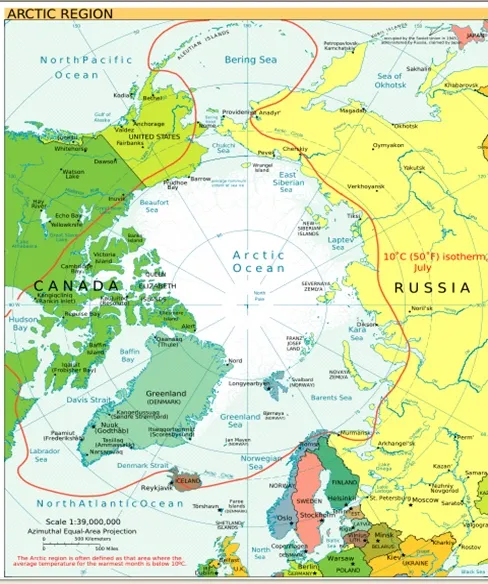
Arctic & Antarctica
SYMBOL : A
CHARACTERISTICS
Cold & Dry.
Weather Fine in high latitude with small amount of cloud.
Bitterly cold.

D)
SOURCE REGIONS
The oceans between Latitudes 15° N – 45° N & 15° S – 45° S.
AIR MASS: MARITIME TROPICAL
SYMBOL: mT
CHARACTERISTICS
Warm, Moist.
When moves to high latitudes over land cooled from below & becomes relatively stable.
Stratiform cloud commonly develops.
E)
SOURCE REGIONS
Land mass of Asia, North Africa & North America. In SH only interior of South America, South Africa & Australia as land mass is less.
AIR MASS: CONTINENTAL TROPICAL
SYMBOL: cT
CHARACTERISTICS
Warm, Dry & Unstable.
When moves to high latitudes over land cooled from below & becomes stable.
Over sea becomes more unstable as it absorbs moisture.
F)
SOURCE REGIONS
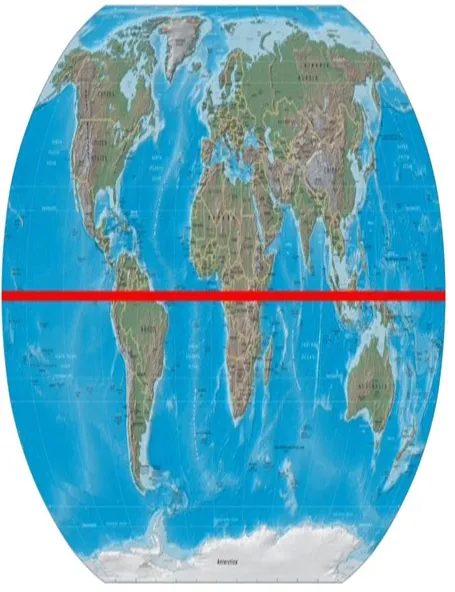
Equatorial area of the TRADE WIND belts.
AIR MASS: EQUATORIAL
SYMBOL: E
CHARACTERISTICS
Hot & Very Humid.
Remains in the Equatorial belt due Low Pressure & light winds. During SW Monsoon often moves up to 35° N over India.
Due high surface heating of the region high instability exists.
Cumuliform clouds with heavy showers.