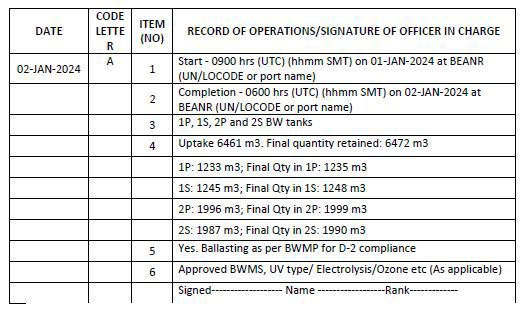
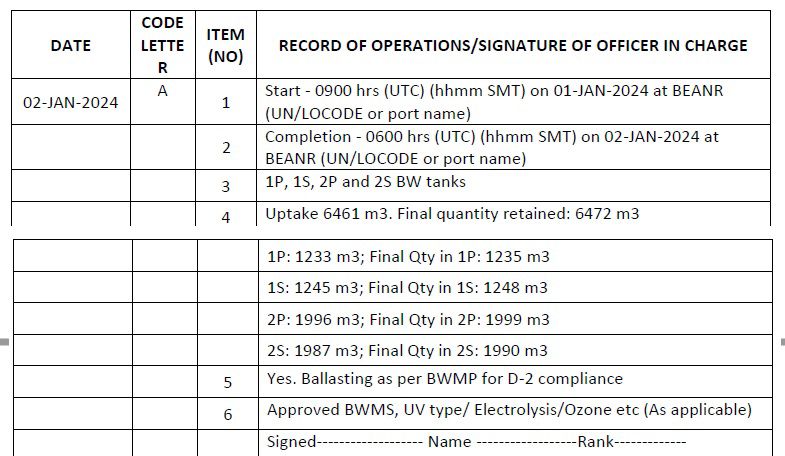
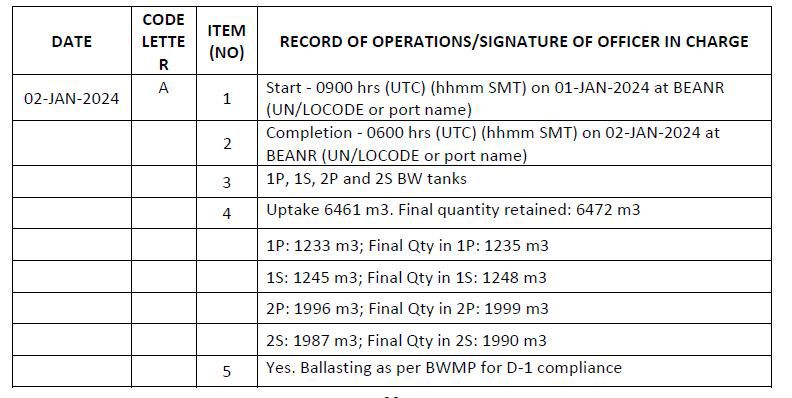
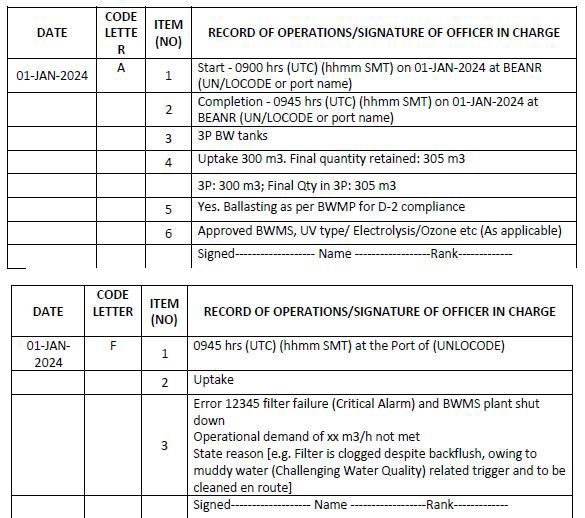
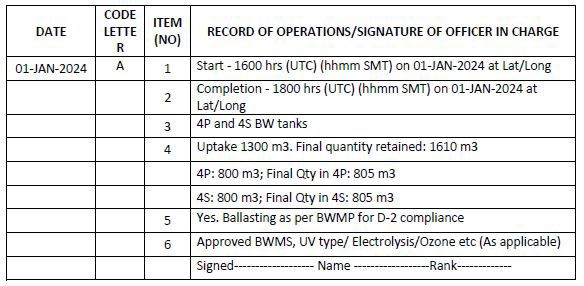
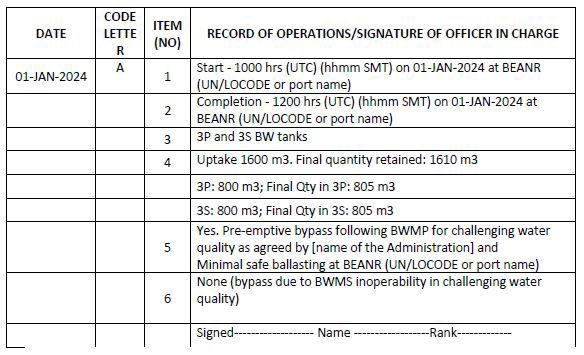
Code A – When ballast water is taken on board from the aquatic environment (ballasting operation)
1. Start time and location (port of uptake or latitude/longitude)
2. Completion time and location (port of uptake or latitude/longitude and minimum depth of water during uptake)
3. The identity of the tanks affected
4. Estimated volume of uptake and final total quantity retained in cubic metres
5. Whether conducted in accordance with the approved Ballast Water Management Plan
6. Ballast water treatment method
Example 1: When ballast water is taken on board (ballasting operation) – at port using BWMS where treatment is done during ballasting
Example 2: When ballast water is taken on board (ballasting operation) – at sea using BWMS where treatment is done during ballasting
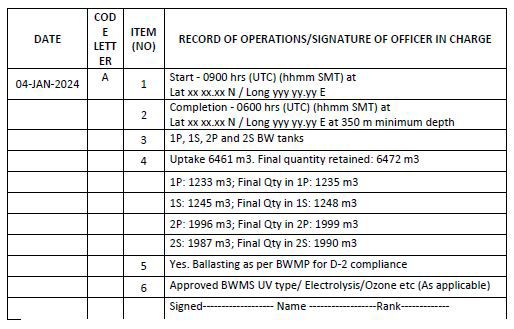
Notes for examples 1 and 2:
1. A ship required to meet the D-1 standard that loads ballast water without treatment in accordance with the BWMP should record “Yes, Ballasting done as per the BWMP for D-1 compliance” in item 5 and “None” in item 6. When the ship later carries out a ballast water exchange, this should be recorded under code C.
2. The examples 1 and 2 consider the new intake water of 6,461 m3 taken in tanks having existing treated water of 11 m3. Mixing of treated water with untreated water will result in the full load being considered as unmanaged (untreated).
3. In case the ship has to take in ballast water that is not being managed as per the approved Ballast Water Management Plan, item 5 should state “No”, item 6 should state “None” and the reason should be given.
4. In the event of the ship carrying out operations as per the approved BWMP, item 5 should state “Yes. Following approved BWMP for (state the contingency measures)” and item 6 should state “None (state action taken and reason)”.
Example 3: When ballast water is taken on board (ballasting operation) – (at sea or in port) on board ships employing in-tank or in-voyage treatment in accordance with the approved Ballast Water Management Plan (where the treatment is done after taking ballast in the tank)
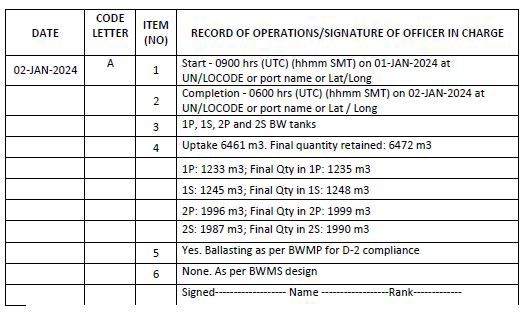
Notes for example 3:
1. BWMS employing “in-tank” treatment load in ballast directly into the tank without any treatment. At the point of uptake, entry to be made as per example 3 & Item 6 must state “None. As per BWMS design”.
2. Subsequently the ship must make entry as per example 10 when carrying out the in-tank or circulation using code C 2
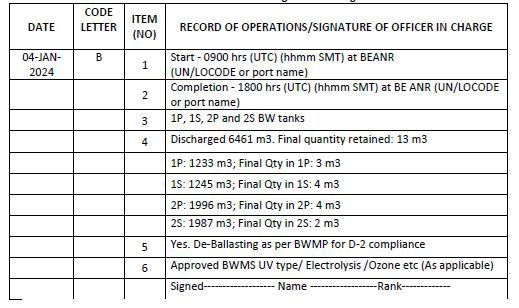
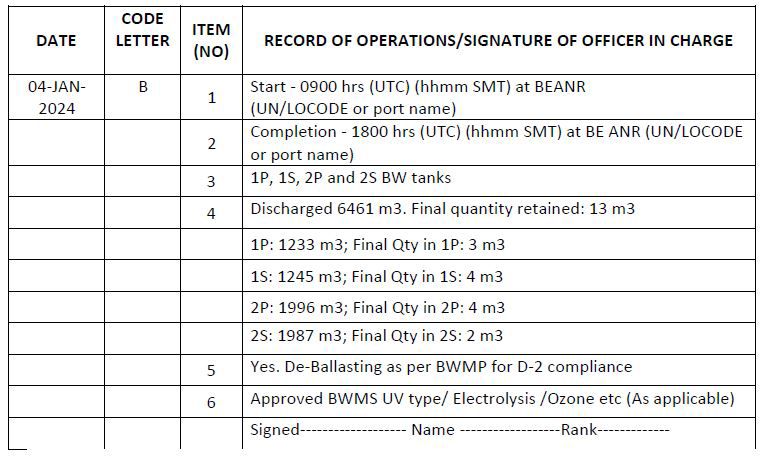
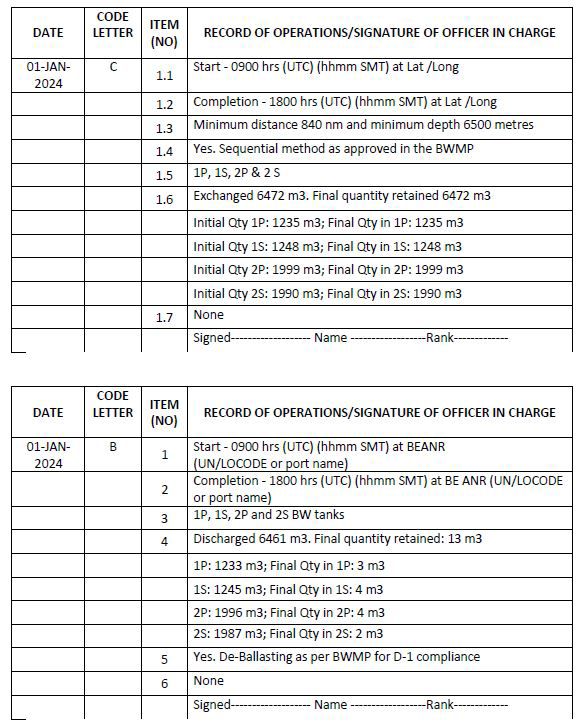
Code B – When ballast water is discharged into the aquatic environment (deballasting operation)
1. Start time and location (port of discharge oS latitude/longitude)
2. Completion time and location (port of discharge or latitude/longitude and minimum depth of water during discharge)
3. The identity of the tanks affected
4. Estimated volume of discharge and final total quantity retained in cubic metres
5. Whether conducted in accordance with the approved Ballast Water Management Plan
6. Ballast water treatment method
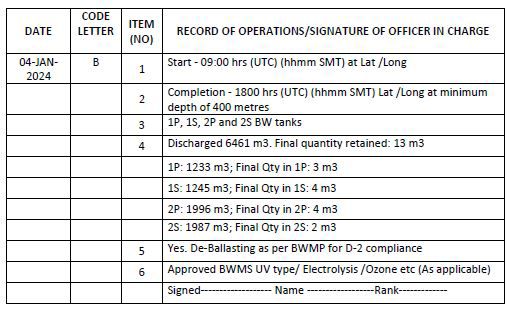
Example 4: When ballast water is discharged into the port (aquatic environment) using BWMS where treatment is done during de-ballasting
Example 5: When ballast water managed as per BWMP is discharged into the sea (aquatic environment) using BWMS where treatment is done during de-ballasting
Notes
1. For a D-1 certified ship, item 5 to be entered as “Yes. D-1 compliant” and item 6 to be entered as “No”.
11
2. Ships employing single pass treatment system (only on uptake) with no treatment during de-ballasting are to record “None, as per BWMS design” in item 6. 3. Ships de-ballasting water managed under the contingency plan of the approved BWMP to record as per example 7
Example 6: When ballast water not managed as per BWMP is discharged At Sea (aquatic environment) without using BWTS
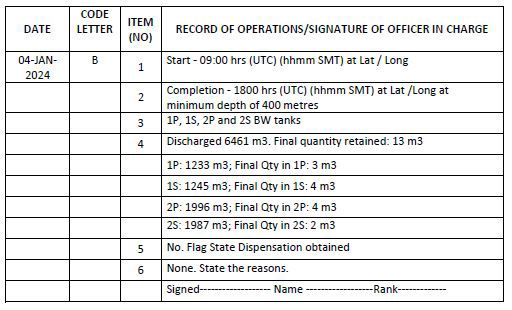
Notes for example 6: For a D-1 certified ship, in case the ship has not carried out the exchange, item 5 to be recorded as “No.” and item 6 as “None. [regulation B-3]”. For a D-2 certified ship, in the event of discharge of semi / untreated water where the approved BWMP process is not followed, the deballasting event must be recorded with item 5 entered “No.” and item 6 entered as “None” and state the reasons. Further, entry using code (F) or code (H) is required to be made (as applicable) preceding the above example 6 entry, stating the conditions leading to non-compliant discharge.
Example 7: When ballast water is discharged into the aquatic environment At Port which has been managed as per the contingency plan in the approved BWMP

For a D-2 certified ship, only in case the ship has implemented contingency plan as per approved BWMP, item 5 to be recorded as “Yes. As per approved contingency plan” and item 6 as “Approved BWMS” (if applicable to the contingency plan procedure adopted).
Code C – Whenever ballast water is exchanged, or treated in-tank or treated through internal circulation
(C) 1 Ballast water exchange
1. Start time and location (latitude/longitude)
2. Completion time and location (latitude/longitude)
3. Minimum distance from the nearest land and minimum depth of water during the exchange or, if applicable, identify the designated exchange area in accordance with regulation B-4.2
4. Whether conducted in accordance with the Ballast Water Management Plan and state the ballast water exchange method (sequential or flow-through or dilution) used
5. The identity of the tanks affected
6. Total quantity exchanged and final total quantity on board in cubic metres
7. Treatment method for the incoming ballast water
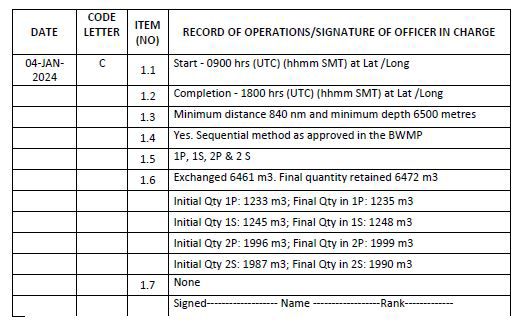
Example 8: Whenever ballast water is exchanged (without any treatment)
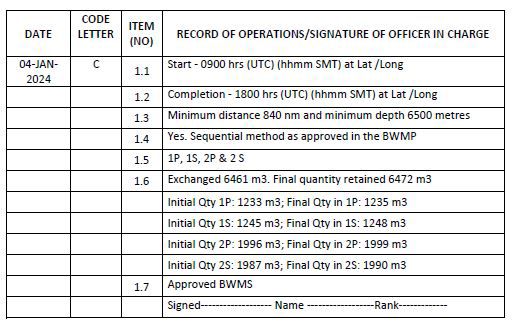
Example 9: Whenever ballast water is exchanged along with treatment using approved BWMS
Notes for examples 8 and 9:
1. The stated exchange method (dilution/sequential/flow-through) must be as per the approved Ballast Water Management Plan.
2. The exchange along with treatment (BWE+BWT), if carried out as per the approved BWMP contingency plan, must be recorded using example 9 and if applicable reported to the concerned authorities prior to discharge of this water.
3. In case of carrying out exchange at a designated area, state the “area name or Lat / Long” under item 1.3 and enter “designated area in accordance with regulation B-4.2” under item 1.4.
4. In the event the ship is unable to carry out exchange owing to safety or operational issues, entry has to be made as per example 26.
In case of a flow-through or dilution ballast water exchange as per approved BWMP
Item 1.4 should state “yes flow-through or dilution (as appropriate) method (as approved in Ballast Water Management Plan)” and under
Item1.6 enter the total quantity exchanged and final quantity retained (example: “exchanged 22000 m3 retained 7200m3”)
(C) 2 Ballast water internal circulation for treatment or in-tank treatment
1. Start time
2. Completion time
3. The identity of the tanks affected (identifying source and destination tanks if applicable)
4. Total quantity treated (through circulation or in tank) in cubic metres
5. Ballast water treatment method
Example 10: Ballast water internal circulation for treatment using approved BWMS
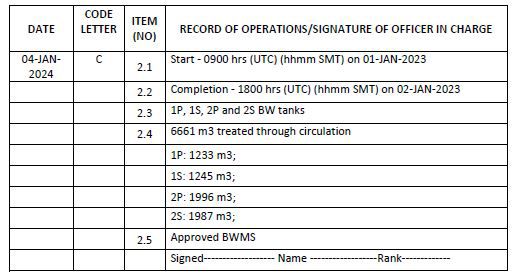
Notes for example 10:
1. The above entry is applicable to the ships which circulate the water in the ballast tanks through the BWMS to achieve treatment. In such case there is no fresh intake or release of ballast water.
2. Ships taking in water directly (bypassing BWMS) and subsequently carrying out treatment in tank or in voyage as per BWMP, are required to make entry as per example 3 after uptake and as per example 10 when the treatment of this water is carried out.
3. Anti-heeling tank automatic operations of transfers of water for the purpose of list correction are not to be recorded under code C.
4. The internal transfers between a set of ballast tanks having same quality of water (either managed or unmanaged) for which entries have already been made under code A or managed under code C are not to be recorded.
5. In case of water being transferred into a tank not accounted under A 3 , C 1.5 or C 2.3, entry is required to be made under code C 2 with C 2.3 capturing the required details.
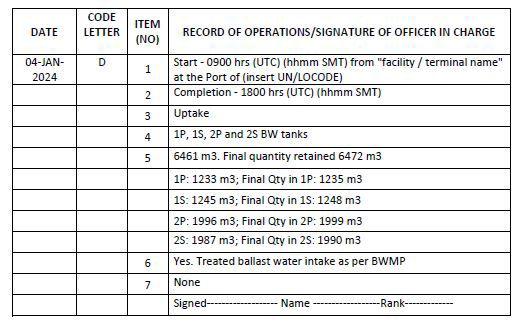
Code D – Uptake or discharge of ballast water from/to a port-based or reception facility
1. Start time and location of uptake/discharge (state facility name)
2. Completion time
3. Operation carried out (whether uptake or discharge)
4. The identity of the tanks affected
5. Total quantity in cubic metres and final quantity retained on board
6. Whether conducted in accordance with the approved Ballast Water Management Plan
7. Onboard ballast water treatment method
Example 11: Uptake of ballast water from a port-based or reception facility
Example 12: Discharge of ballast water to a port based reception facility.
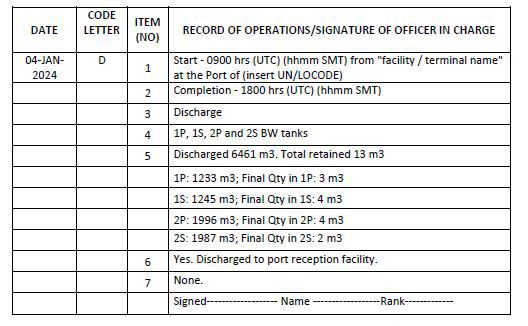
Notes for examples 11 and 12:
1. The ship taking in ballast water from the port facility which is treated by the onboard BWMS prior to filling the ballast tanks is to enter item 7 as “Yes, approved BWMS” in example 11.
2. The documents concerning the uptake / discharge of ballast water provided by the port-based or reception facility must be attached to the BWRB and must be readily available for inspection.
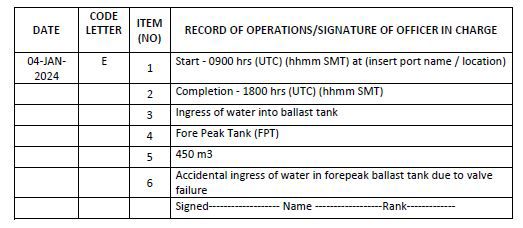
Code E – Accidental discharge/ingress or other exceptional uptake or discharge of ballast water
1. Start time and location of ingress/uptake/discharge (port name or latitude/longitude)
2. Completion time
3. Operation carried out (whether ingress, uptake or discharge)
4. The identity of the tanks affected
5. Total quantity of ballast water in cubic metres
6. State the circumstances of ingress, uptake, discharge or loss, the reason thereof, any treatment method used and general remarks
Example 13: Accidental ingress of ballast water
Example 14: Accidental discharge of ballast water
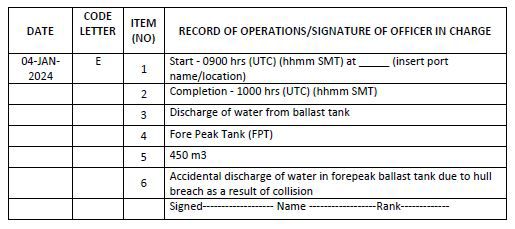
Example 15: Exceptional uptake of ballast water
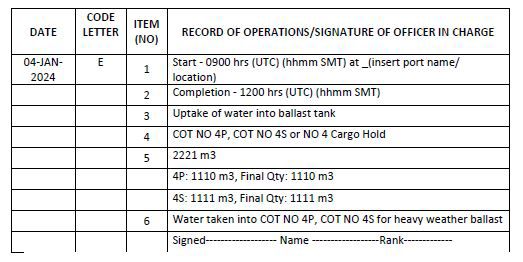
Notes for examples 13, 14 and 15:
1. Accidental ingress or discharges are occurrences without human initiation. Water ingress or discharge (escape) due to collision, grounding, structural failures, valve or machinery failures are to be recorded under code E.
2. Exceptional uptake or discharge are human initiated procedures undertaken in exceptional circumstances for the safety of the ship and prevention of pollution.
3. Intake of shore-supplied untreated water into ballast tanks at a dry dock facility for the purpose of undocking ship should be considered as exceptional circumstance and entry recorded under code E.
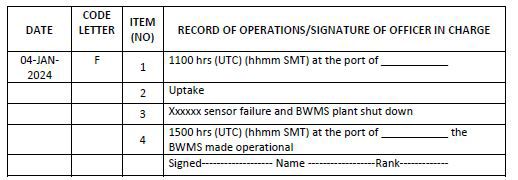
Code F – Failures and inoperabilities of the Ballast Water Management System (BWMS)
1. Time and location (port name or latitude/longitude) of failure of the BWMS
2. Operation carried out (state whether uptake or discharge)
3. Description of the issue (e.g. kind of alarm or other description of circumstances)
4. Time and location (port name or latitude/longitude) when the BWMS has been made operational
Example 16: Failures of the BWMS that are repaired immediately
Example 17: Inoperabilities of the Ballast Water Management System
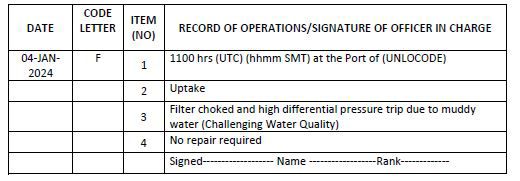
Notes for examples 16 and 17:
1. Failures and inoperability include malfunctions, shutdowns or critical alarms indicating a failure of the ballast water management system which may indicate non-compliance with the D-2 standard (except routine information and warnings).
2. In case the BWMS failure is not rectified immediately, the entry using code F / item 4 is to be made on the date when the BWMS is made operational.
3. In the event of failure of the BWMS during ballasting or deballasting, the entry under code A or code B must be followed up by code F entry as per example 17.
4. Inoperability of the BWMS due to challenging water conditions is required to be recorded under code F items 1, 2 and 3 with remark in item 3 clearly stating the alarms which are triggered owing to challenging water conditions.
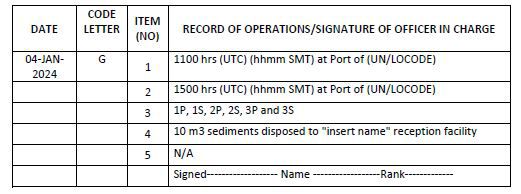
Code G – Ballast tank cleaning/flushing, removal and disposal of sediments
1. Time and ship’s location on commencement of ballast tank cleaning/flushing, removal or disposal of sediments (port name or latitude/longitude)
2. Time and ship’s location on completion of ballast tank cleaning/flushing, removal or disposal of sediments (port name or latitude/longitude)
3. Tank(s) identification (name of the ballast tanks as per the Ballast Water Management Plan)
4. Discharge or disposal to a reception facility (state quantity in cubic metres and name of the facility)
5. Disposal or discharge to the aquatic environment as per Ballast Water Management Plan (state quantity in cubic metres, minimum distance from the nearest land in nm and minimum depth of water in metres)
Example 18: Ballast tank cleaning and discharge of sediments to reception facility / dry dock
Example 19: Ballast tank cleaning/flushing and disposal of sediments to aquatic environment (at sea)
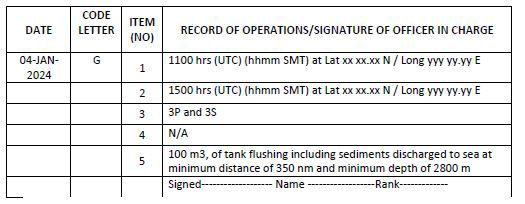
Notes for examples 18 and 19:
1. Sediment disposal receipt provided by shore/port reception facility or dry dock facility must be attached to the BWRB and must be available for inspections.
2. In case of flushing of a tank with treated water, operation to be recorded under code G items 1, 2, 3 and 5 with comments in 5 stating that treated water was used to flush the tank.
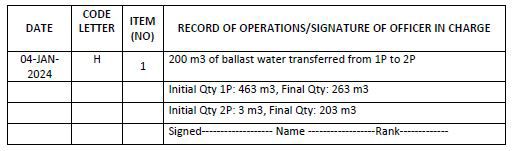
Code H – Additional operational procedures and general remarks Example 20: Internal tank-to-tank ballast water transfers
Example 20: Internal tank-to-tank ballast water transfers
Example 21: Sampling of ballast water during discharging

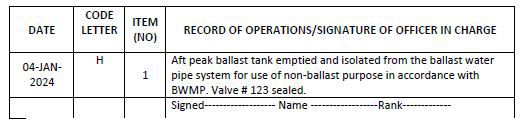
Example 22: Use of ballast water tank for non-ballast water purpose: taking out of operation (For eg Collection of Treated Sewage as per Approved plan)
Example 23: Use of ballast water tank for non ballast water purpose: taking into operation

Example 24: Reporting to Flag or Port State of a failure of the BWMS

Note for example 24:
1. BWMS failures are recorded under code F. In case of reporting to flag or port State, above entry to be recorded and, if operations subsequently carried out as per contingency plan or as per advice from port/flag State, same to be recorded under applicable code/item.
Example 25: Entry pertaining to an earlier missed operational entry
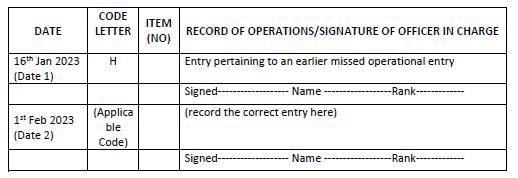
Note for example 25:
1. This entry is to be followed by the entry pertaining to the missed operation. The date 1 to be entered corresponding to the original date of operation and subsequent entry date 2 to be the current date.
Example 26: Ship unable to perform ballast water exchange owing to safety reasons, e.g. bad weather

Note for example 26:
1. This entry is to be made for safety (bad weather) or operational related issues (e.g. ship’s route does not pass through areas where distance from nearest land is always more than 50 nm and / or 200 m depth or a designated BWE area).
Example 27 : Scenarios for making sequential entries in the ballast water record book
a. Scenario 1: Uptake and discharge of ballast water for a ship subject to regulation D-2
b. Scenario 2: Uptake, exchange and discharge of ballast water for a ship subject to regulation D-1
c. Scenario 3: Dealing with ports with challenging water quality employing reactive bypass
Sequence of events:
I. Ballast water uptake, interruption due to water quality, BWMS bypassed and uptake of minimal (safe) ballast water completed.
II. BWMS repaired, if applicable.
III. Ship completes remaining ballasting at nearby location.
IV. Exchange + treatment undertaken with tank flushing.
V. Discharge of ballast water at receiving port.
I. Uptake of minimum ballast water at the port with CWQ
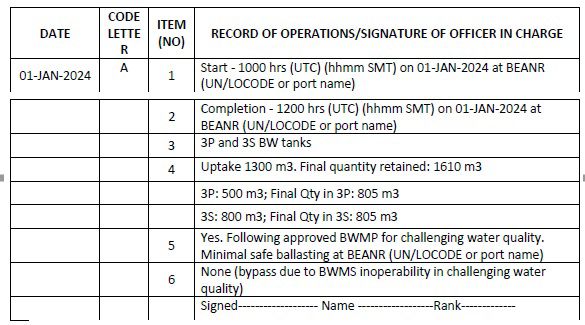
(Note: If the unmanaged ballast water is mixed with the managed ballast water, as in this example, the whole quantity must be considered as unmanaged and action taken accordingly.)
II. Corrective action or maintenance

III. Uptake of remaining ballast water through the BWMS
IV. Exchange + treatment undertaken with tank flushing
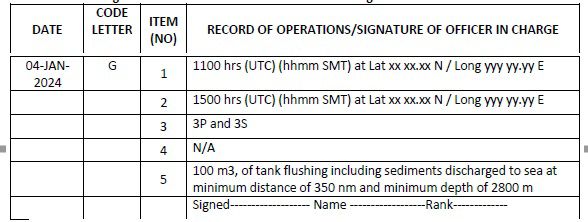
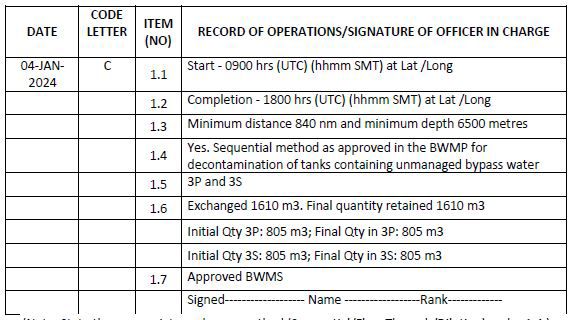
(Note: State the appropriate exchange method (Sequential/Flow Through/Dilution) under 1.4.) (Note: The above two entries are concerning the BWE+BWT process, in which the tank flushing is part of the operation. In case that tank flushing is not carried out, the Code G entry would not be required to be made.)
V. Discharge of ballast water at receiving port
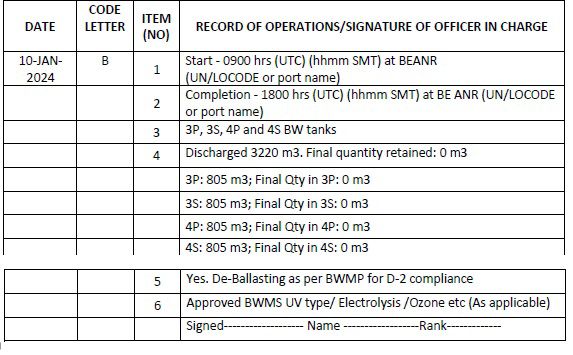
d. Scenario 4: Dealing with ports with challenging water quality employing pre-emptive bypass Sequence of events:
I. Ballast water loading: BWMS bypassed pre-emptively and loading of minimal ballast water completed.
II. Not applicable.
III. Ship completes remaining ballasting at nearby location.
IV. Exchange + treatment undertaken with tank flushing.
V. Discharge of ballast water at receiving port.
Notes:
Pre-emptive bypass is valid when agreed by the Administration and the port State receiving the subsequent discharged water after the CWQ measures are implemented, as stated in the BWMP. The ship to make subsequent entries as per (c), (d) and (e) mentioned under scenario 3.