Free water.
The measured volume of water in a tank not in suspension with the liquid in the tank at observed temperature. Expressed in cubic meter or/and barrels.
Total Observed Volume (TOV).
The total measured volume of all petroleum Iiquids,BS&W,and free water at observed temperature.Expressed in cubic meter orland barrels.
Gross Observed Volume (GOV).
The total volume of all petroleum liquids and BS&W,but observed temperature. Expressed in cubic meter or/and barrels.
GOV = TOV -Free Water
Net Observed Volume (NOV).
The total volume of all petroleum products but excluding free water and BS&W at observed temperature.
Expressed in cubic meter and/or barrels.
NOV = TOV -Free Water -BS&W
NOV = GOV -BS&W
Gross Standard Volume (GSV).
The total volume of all petroleum products and BS&W,but excluding free water corrected by the appropriate volumecorrectionfactor (VCF) for observed temperature and density to a standard temperature. Expressed in cubic meter or barrels.
GSV = GOV x VCF
GSV = GOV at 15°C/60°F
Net Standard Volume (NSV).
The total volume of all petroleum products excluding BS&W and free water corrected by the appropriate volumecorrectionfactor (VCF) for observed temperature and density to a standard temperature. Expressed in cubic meter and/or barrels.
NSV = NOV x VCF
NSV = NOV at 15°C/60°F
Total Calculated Volume (TCV)
The total volume of all petroleum products and BS&W corrected by the appropriate volume correction factor for observed temperature and standard temperature and all free water at observed temperature.
Expressed in cubic meter and/or barrels. .
TCV = GSV + Free Water
Bottom Sediments and Water (BS&W).
Quantity of sediments and water into the total amount of petroleum products.
Expressed as a percentage as determined by tests.
Observed Temperature.
Temperature of cargo measured at various places in the tank. Mean temperature is determined.
Standard Temperature.
Temperature of 15°c in the metric system,or 60°F in the American system.
All volumes must be converted to this temperature before comparing.
Relationship: density, specific density , API Gravity
Gravity is a mass-per-unit-volume relationship.
With petroleum products the relationship is expressed as specific gravity.
The following definition applies:
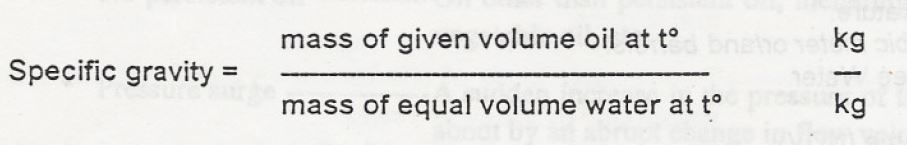
Temperature normally equal to 60°F or 15°c.
Specific gravity is sometimes called relative density.

Specific gravity is being replaced by density expressed in kg per m3.
The following definition applies:
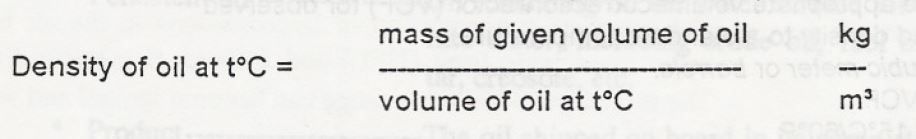
In the USA the API gravity is being used. API gravity is an arbitrary scale, calibrated in degrees and related to the specific gravity by the following relation’:

Mass and weiqht relationship.
Mass
The mass of a substance is the quantity it contains. It is independant of external conditions.ln oil measurement, it is often referred to as weight-in-vacuo. The metric unit is the kg where 1000kg equals 1 metric tonne.
Following relationship applies:
mass ofoil =volume of oil at t°C x oildensity at t°C
Weight.
The weight of a substance (calledweight-in-air)isthe mass which a substance appears to have when weighted in air.
The weight is calculated using the following equation:
weight of oil =volume of oil x weight correction factor
Weiqht Correction Factor (WCF).
The weight correction factor must be obtained from the appropriate table in the Petroleum Measurement Tables.
In the American system the WCF can be obtained from table II “Long tons per barrel at 60°F against API gravity at 60°F”.
In the metric system the WCF can be obtained from table 56 “Kilograms per liter at 15°C and liters at 15°C per metric ton against density at 15°C”.
The WCF can be easily obtained by subtracting 0.0011 kg/l from the density at 15°C.
Unfortunately it is much easier to subtract than to consult Table 56.This has led to the problem that it is no longer obvious which density is used: the density or the WCF.
Unit Conversion.
Units can be easily interchanged by using the approprtate table from petroleum measurements Table Vol XI “Entry with API” or Vol XII “Entry with Relative Density”.
It is extremely important however to be aware of the following fact: “Like can only be compared with like”.
Comparasion between volumes and capacities must be done at the same temperature.
Cargo Calculations.
Metric system.
Schematic layout of calculations.
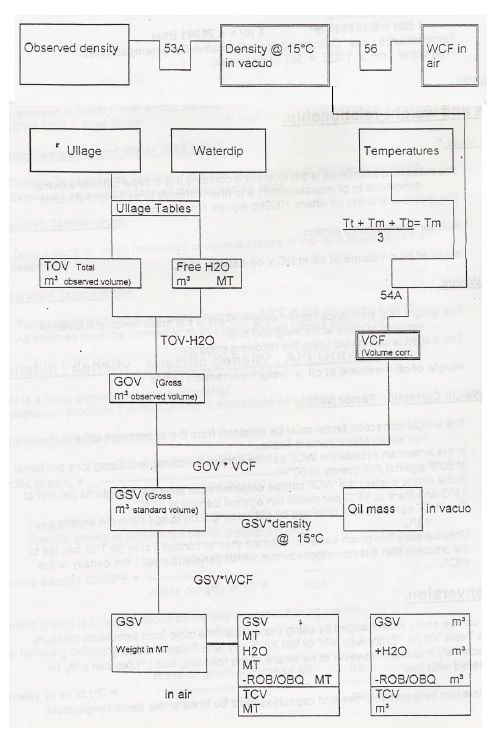
Notes:
– Given: TOV -Free Water – Temperature and Observed Density
– Can be calculated
1) weight in air (mt) (and in LT if needed)
2) weight in vacuo ( = oil mass)
-Tabies used: 53A -56 -54A
-The relationship between barreis and cubic meters is very precise if same temperatures are used”
1 Bbl = 0.158987 m3
1 m3 = 6.28981 Bbls
-Temperatures: see “Calculating Representative Cargotemperatures”.
-Free water: m3 x 1.025 = MT (if seawater)
Example :
-TOV: 100000m3 at 30°C Density: 0.8520 at 15°C
VCF from Tab!e 54A: 0.9873 t
WCF from Table 56 : 0.8509
-GSV = 100000 x 0.9873 = 98730 m3
-Weight in vacuo = 98730 x 0.8520= 84117.96 MT (= oil mass)
-Weight in air = 98730 x 0.8509 = 84009.36 MT
General remark concerning metric calculations:
In the metric system both weight in air and weight in vacuo can be easily calculated.
But this can lead to confusion if calculation form is not clearly labelled.
Table 53A: Generalized crude oils.Correction of observed density to density 15°C,
Table 54A: Generalized crude oil.Correctionof volume to 15°C(againstdensityat 15°C).
Table 56: Kilogram per liter at 15°C and liters at 15°C per MT against density at 15°C,
American system.
Schematic layout of calculations:
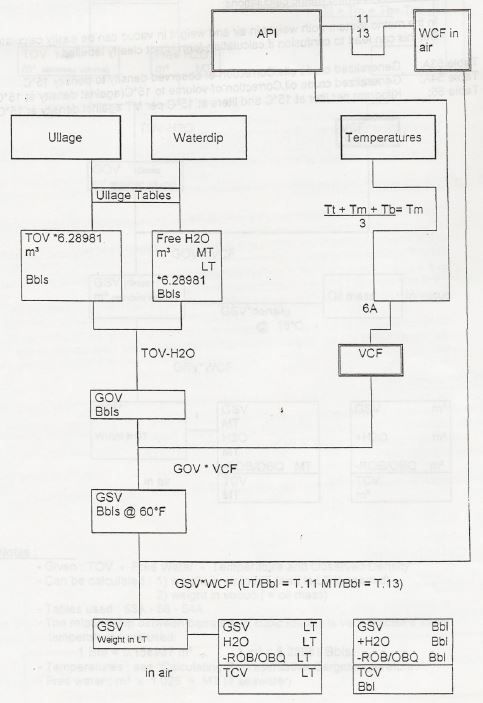
Notes:
-Temperature: see” Calculating Representative Cargo temperatures”.
-Oil weight is calculated ( weight in air) : oil mass can only be calculated by converting API to density and to preform the metric system calculation.
-For calculations in LT table II must be consulted for calculations in metric ton table 13.
-If in LT the free water must also be converted to L1. ( LT = MT x 1.016047)
-The calculations for LT are the most accurate.
Example
-TOV = 100000 m3
-TOV=628981 Bbls at 86°F API 34,49
-VCF from Table 6A : 0.9877
-WCF from Table 11 : 0.13309
-WCF from Table 13: 0.13520
-GSV = 628981 x 0.9877 = 621244.54 Bbls
-Weight in air = 621244.54 x 0.13309 = 82681.4 LT
= 621244.54 x 0.13520 = 83992.3 MT
(If formula for LT / MT -conversion is being used, a tonnage of 84008.2 MT is found a difference of about 16 MT)